
Mechanical seal is an axial end face sealing device that relies on elastic elements to pre tighten the sealing pair, and under the joint action of medium and elastic element pressure, the sealing pair is compressed to achieve sealing. Its structure is shown in Figure 1. Sealing rings are divided into two types: moving rings and stationary rings, and are the most important components that make up mechanical seals. The working condition of the sealing ring determines the performance and service life of the mechanical seal, and the performance of the sealing ring material directly affects the working condition of the sealing ring. Therefore, understanding the requirements of mechanical seals for the performance of sealing materials and selecting appropriate sealing materials are key to ensuring the safe operation of mechanical seals.
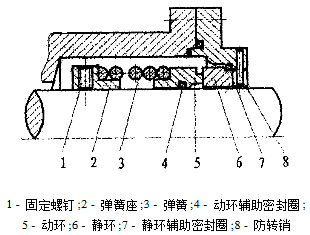
Figure 1 Basic Structure of Mechanical Seal
1 Performance requirements for sealing secondary materials in mechanical seals
In order to ensure the normal operation of the sealing ring in the mechanical sealing device, considering factors such as reducing wear, corrosion resistance, and preventing biting, the sealing ring is often configured as a pair of hard and soft rings with different hardness. The hard ring is usually a moving ring, and the performance of the hard ring material is required as follows:
1) Sufficient strength and stiffness
Under working conditions such as pressure, temperature, and sliding speed, the ring should not be damaged, and deformation should be minimized as much as possible. The sealing performance should still be maintained when the working conditions fluctuate.
2) Good tribological properties
During operation, the sealing ring end faces are always in contact and rotating state. Therefore, it is required that the sealing ring material has good wear resistance, and maintain good lubrication performance of the fluid film and good boundary lubrication performance to ensure satisfactory service life under working conditions.
3) Good thermal conductivity, heat resistance, and heat shock resistance
During operation, due to poor lubrication conditions between the sealing surfaces and the temperature of the sealing fluid itself, the sealing ring is at a high working temperature. In addition, there may be rapid temperature changes. Therefore, it is required that the material has a high thermal conductivity and a small linear expansion coefficient, and should not crack when subjected to thermal shock.
4) Good corrosion resistance
A sealing ring with good corrosion resistance can resist the corrosion and wear of fluids, resulting in a long working life.
In addition to the above performance, the hard ring should also have good formability and processability, low density and low permeability, and good self-lubricating properties.
No material can fully meet all the above requirements. Usually, the main performance requirements for sealing materials are proposed based on the usage environment, and suitable materials are selected accordingly.
Types, characteristics, and properties of silicon carbide
Currently, nearly half of the mechanical seal end face materials used in industrial production use silicon carbide. There are many manufacturing methods for silicon carbide, and their properties are also different. According to different manufacturing methods, there are several types: atmospheric pressure sintered silicon carbide, reaction sintered silicon carbide, hot pressed sintered silicon carbide, chemical vapor reaction silicon carbide, and chemical vapor deposition silicon carbide. As mechanical sealing materials, the first three are the most commonly used.
2.1 Types and characteristics of silicon carbide materials for mechanical seals
1) Atmospheric pressure sintering of silicon carbide
Using powder metallurgy manufacturing method, the raw material is submicron sized silicon carbide particles, which are sintered without applying pressure, and the sintering density can reach 95% of the theoretical density. Sintering is carried out under inert gas protection or in vacuum at temperatures between 1900 and 2200 ℃, typically with the addition of boron and carbon as sintering aids. After molding and sintering, silicon carbide particles form integral silicon carbide components. Atmospheric pressure sintered silicon carbide is the hardest and most corrosion-resistant sealing material among all silicon carbide, therefore it is widely used in mechanical seals.
2) Reaction sintered silicon carbide
Reacting porous carbon profiles with molten silicon and sintering them into integral silicon carbide. This type of silicon carbide contains about 10% to 12% free silicon, which plays a good role in reducing friction and wear. The corrosion resistance of this silicon carbide material is inferior to that of atmospheric pressure sintered silicon carbide, but due to its excellent sealing pair with carbon graphite, API682 specifies that this sealing pair should be preferred.
3) Hot pressed sintered silicon carbide
By granularity≤ 1μ M silicon carbide powder with appropriate additives is loaded into a graphite mold and produced in a hot pressing furnace at 2000-2100 ℃ under pressure of 30-50MPa. Hot pressed sintered silicon carbide is the most chemically stable type of silicon carbide and is used as a sealing surface material for corrosion-resistant sealing pairs.
2.2 Performance of Silicon Carbide Materials for Mechanical Seals
The properties of silicon carbide ceramic materials may vary with different preparation processes. Table 1 compares the properties of three different silicon carbide materials prepared by different processes, and compares them with tungsten carbide, which is commonly used as a sealing material.
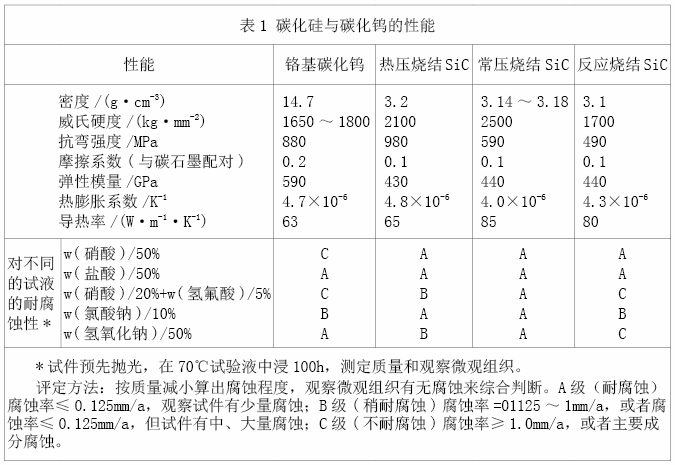
Table 1 Properties of Silicon Carbide and Tungsten Carbide
According to Table 1, compared with tungsten carbide, silicon carbide has lower density, better corrosion resistance and thermal performance, and lower friction coefficient, which gives it significant advantages in mechanical seal materials. One of the most noteworthy excellent properties of silicon carbide materials is their extremely high hardness, making them widely used as mechanical seal hard rings.
Application of Silicon Carbide in Mechanical Seals
Due to the excellent performance required for mechanical sealing, silicon carbide materials can be applied in operating conditions such as high pressure, high speed, high temperature, corrosive media, and media containing solid particles.
3.1 Silicon carbide is used for high PV mechanical seals
PV value refers to the product of the sealing fluid pressure P and the average sliding velocity V of the sealing end face, which represents the limit value of mechanical seal use and is an indicator to measure the working ability of mechanical seals. High fluid pressure and high rotational speed result in high PV values for mechanical seals.
1) High fluid pressure
When working under high pressure, a large load must be applied to the end face of the mechanical seal, and the end face compressive stress is very high, which requires the sealing material to have high strength and stiffness. Silicon carbide material is a material with high strength and stiffness, and its elastic modulus is high, making it difficult to deform under high pressure. At the same time, the compressive strength of silicon carbide is very high. For example, the flexural strength of EkasicD sintered silicon carbide is 410MPa, while the compressive strength is 2200MPa, which is more than 5 times the flexural strength. It can fully withstand high end face stress and meet the requirements of use.
In addition, high end face stress will increase the frictional heat of the end face, thereby raising the temperature of the friction pair, causing the liquid film between the end faces to be destroyed and forming dry friction, which is prone to adhesive wear. Experimental studies have shown that the wear of carbon graphite in the combination of silicon carbide and carbon graphite is very low at various PV values, and its value changes very little with the increase of PV value. This indicates that silicon carbide has strong resistance to adhesive wear and is very advantageous as a high-pressure sealing material.
By using laser processing method, spherical micropores can be machined on the end face of the silicon carbide sealing ring, as shown in Figure 2. Experimental studies have shown that the use of silicon carbide sealing rings with micropores on the end face in combination with carbon graphite can significantly improve the PV value of mechanical seals, and greatly reduce the temperature rise, friction torque, and friction coefficient of the sealing end face.

Figure 2 SiC sealing ring with micropores on the end face
2) High speed
Mechanical seals working at high speeds will mainly suffer from heating, wear, and vibration of friction pairs due to their high linear velocity. Therefore, it is required that the sealing material has a low density and high strength, so that the centrifugal force generated by the rotating ring during high-speed operation is small, and the vibration and deflection caused are also small, thereby maintaining a stable fit of the sealing end face. In addition, the material should have good heat resistance and thermal conductivity to reduce the friction temperature of the mechanical seal, minimize friction wear, avoid thermal cracks and deformation, and enable the mechanical seal to maintain normal operation. According to the properties of silicon carbide materials, silicon carbide sealing rings can fully meet the requirements of high-speed mechanical seals.
3.2 Silicon Carbide Used for High Temperature Mechanical Seals
High temperature can easily cause changes in the performance of friction pair materials, resulting in deformation of the sealing end face, reduced hardness, and a decrease in the service life of mechanical seals. Therefore, the thermal deformation, high-temperature strength, and wear resistance of high-temperature sealing materials are key factors in selecting sealing materials. Silicon carbide has high high-temperature strength, and its bending strength at 1400 ℃ is the same as that at room temperature. Therefore, silicon carbide can be used for mechanical seals under high-temperature conditions.
3.3 Mechanical seals using silicon carbide for corrosive media conditions
Mechanical seals used for corrosive media, corrosion wear is the most common form of material failure in friction pairs. This corrosive effect is extremely strong and can directly or rapidly cause changes in sealing performance. Silicon carbide has good chemical stability, so it can be applied in various highly corrosive acidic and alkaline media. Non pressure sintered silicon carbide and hot pressed sintered silicon carbide are single-phase structures with strong corrosion resistance. Hot pressed sintered silicon carbide still has good chemical stability even at 900 ℃, due to the formation of a protective silicon dioxide film on the surface in an oxidizing atmosphere.
3.4 Mechanical seals using silicon carbide for media containing solid particles
Many sealing fluids in industrial production contain solid particles that are prone to deposit on the friction pair end face. These particles not only cause severe particle wear on the sealing surface, but also generate local heat on the sealing surface, leading to thermal cracking. Silicon carbide not only has high hardness, wear resistance, and resistance to thermal cracking, but also has excellent emergency operation characteristics. Therefore, the application potential of hard sealing pairs paired with silicon carbide itself in granular media is great. Experimental studies have shown that when silicon carbide is used in combination, using ion reaction etching technology to process cylindrical micropores on one of the sealing surfaces can not only reduce the friction coefficient between the sealing surfaces, but also significantly improve the bearing capacity of the sealing surfaces.
4 Conclusion
Silicon carbide has excellent properties such as low density, corrosion resistance, and thermal performance when paired with carbon graphite, as well as low friction coefficient and extremely high hardness when paired with itself. It is fully suitable as a sealing ring material for mechanical seals and is therefore widely used in mechanical seals under high PV values, high temperatures, corrosive media, and media containing solid particles.